v3 Release Notes
Major release focused on extensibility, expanded provider support, and enhanced user experience.
🚀 What's New at a Glance
| Feature | Description |
|---|---|
| 530+ Models | Access over 530 models from 24 providers via models.dev integration |
| Model Selector | Redesigned full-featured dialog with search, filtering, sorting, and favorites |
| Extensions | Add features, providers, and customize the UI with a flexible plugin architecture |
| Gemini RAG | Manage Gemini File Search Stores and manage document uploads for RAG workflows |
| Tool Support | First-class Python function calling for LLM interactions with your local environment |
| MCP Support | Connect to Model Context Protocol servers for extended tool capabilities |
| Computer Use | Desktop automation - control mouse, keyboard, and take screenshots like a human |
| KaTeX Math Typesetting | Support for beautiful rendering of LaTeX math expressions |
| Calculator UI | Beautiful UX Friendly UI to evaluate python math expressions |
| Run Code UI | Execute Python, JS, TypeScript and C# code scripts in a CodeMirror editor |
| Image Generation | Built-in support for Google, OpenAI, OpenRouter, Chutes, and Nvidia |
| Audio Generation | TTS support for Gemini 2.5 Flash/Pro Preview models |
| Media Gallery | Beautiful UI to browse generated images and audio generations |
| SQLite Storage | Migrated IndexedDB to server SQLite for robust persistence and concurrent usage |
| Asset Caching | Persistent image/file file caching with metadata |
| Gemini RAG Extension | Manage Gemini File Search Stores for RAG workflows with document uploads and sync |
Table of Contents
- New Model Selector UI
- Rewritten for Extensibility
- Extensions System
- Gemini RAG Extension
- Tool Support
- MCP Support
- Core Tools
- Computer Use
- Calculator UI
- Run Code UI
- KaTeX Math Typesetting
- Image Generation Support
- Audio Generation Support
- Media Gallery
- System Prompts Library
- Server-Side SQLite Storage
- Image Cache & Optimization
- CLI - More Powerful Than Ever
- Upgrade Instructions
Install
Get instant access to 530+ models from 24 providers with extensibility at its core:
pip install llms-pyUpgrade
pip install llms-py --upgradeSee Install Docs for running from Docker or source.
Switch to models.dev Provider Model Configuration
A major change to significantly increase the available models is the switch to utilizing the same models.dev open provider and model catalogue as used and maintained by OpenCode.
llms.json provider configuration is now a superset of models.dev/api.json where its definitions are merged, allowing you to enable providers using just "enabled": true to inherit the configuration from models.dev
🌐 Expanded Provider Support
The switch to models.dev greatly expands the model selection to over 530 models from 24 different providers, including new support for:
| Provider | Models | Provider | Models |
|---|---|---|---|
| Alibaba | 39 | Hugging Face | 14 |
| Chutes | 56 | Zai Coding Plan | 6 |
| DeepSeek | 2 | MiniMax | 1 |
| Fireworks AI | 12 | Moonshot AI | 5 |
| GitHub Copilot | 27 | Nvidia | 24 |
| GitHub Models | 55 | Zai | 6 |
| Cerebras | 3 | ||
| LMStudio | local | Ollama | local |
Non OpenAI Compatible LLM and Image generation providers are maintained in the providers extension, registered using the ctx.add_provider() API. There are several different provider implementations to take advantage of features available in each provider, such as Interleaved Thinking support in Anthropic's Messages API which enables all Claude and MiniMax models to reason between tool calls for improved agentic performance.
TIP
🔄 Automatic Provider Updates
This actively maintained list of available providers and models are automatically updated into your providers.json daily that can also be manually updated with:
llms --update-providersAs an optimization only the providers that are referenced in your llms.json are saved. Any additional providers you want to use that are not included in models.dev can be added to your ~/.llms/providers-extra.json, which get merged into your providers.json on every update.
This keeps your local configuration file lightweight by only including the providers that are available for use.
Configuration Examples
Enable providers by ID — all configuration is automatically inherited:
{
"openai": { "enabled": true },
"xai": { "enabled": true }
}See Configuration docs for more info.
New Model Selector UI
With over 530 models from 24 providers now available, discovering and selecting the right model required a complete overhaul. The Model Selector has been completely redesigned as a full-featured dialog offering:
- 🔍 Smart Search & Discovery - Instantly search across model names, IDs, and providers
- 🎯 Advanced Filtering - Filter by name, providers & input and output modalities
- 📊 Flexible Sorting - Sort by Knowledge Cutoff, Release Date, Last Updated & Context
- ⭐ Favorites System - Star model card to add/remove to favorites quick list
- 💎 Rich Model Cards - In depth model overview at a glance
Where providers can be quickly enabled or disabled to customize which models are available:
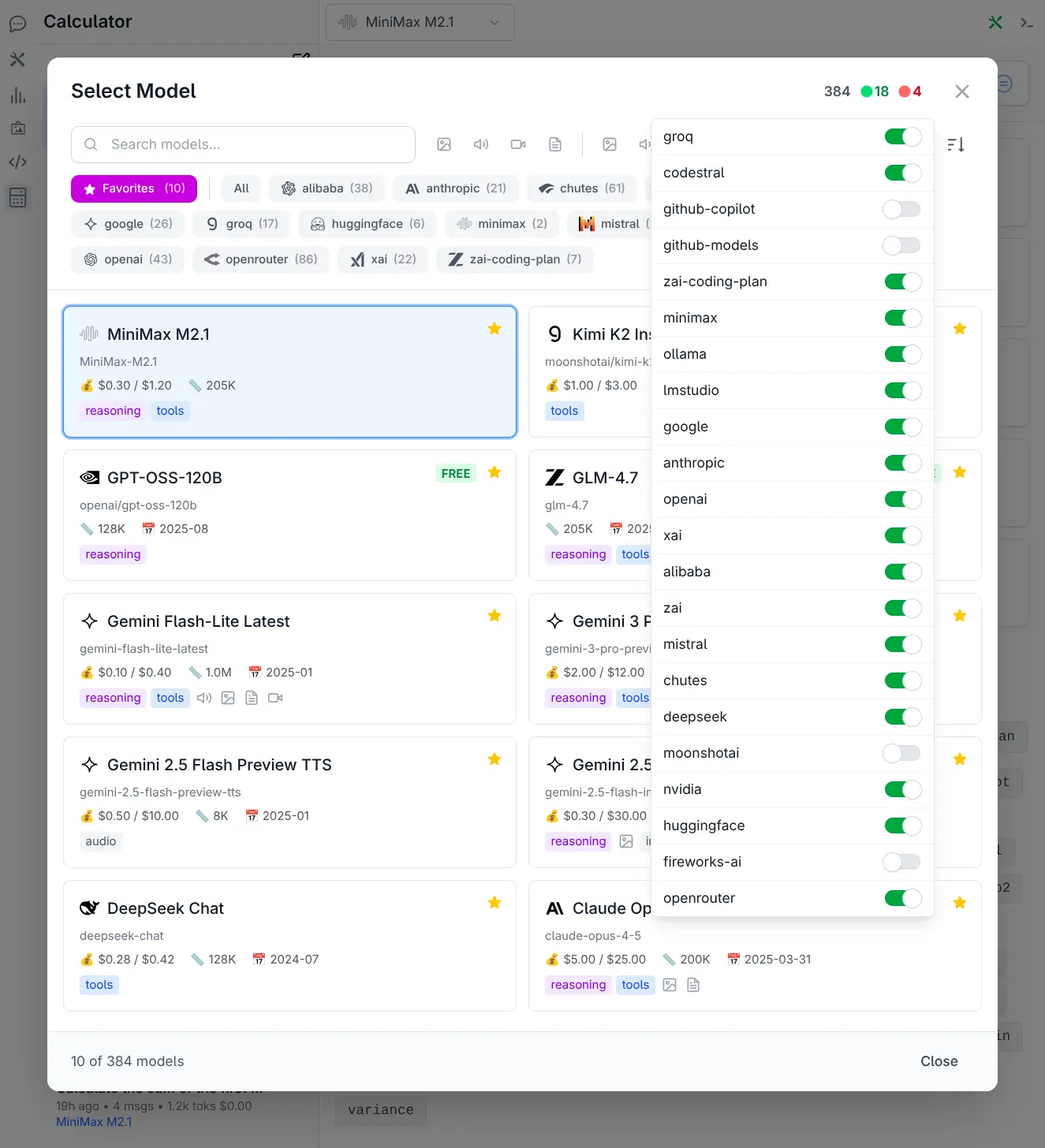
See Model Selector docs for more info.
Rewritten for Extensibility
llms.py has been rewritten from the ground-up with extensibility a core concept where all major UI and Server features now layer on their encapsulated functionality by using the public Client & Server Extensibility APIs.
Extensions are just folders that can add both Server and UI features using the public client and server extensibility APIs. Built-in features are just extensions in the repo's llms/extensions folder which can be disabled or overridden by adding them to your local ~/.llms/extensions folder. Too minimize bloat, only features that are generally useful and don't require additional dependencies are included as built-in extensions.
llms includes support for installing and uninstalling extensions from any GitHub repository. For better discoverability, non built-in extensions are maintained in the github.com/llmspy organization repositories which anyone else is welcome to contribute their repos to for increased discoverability.
UI components are now registered and referenced as Global Vue components, which can be easily replaced by registering Vue components with the same name as done in the xmas extension demo.
This approach allows main.py to retain a lean functional core in a single file whilst still being fully extensible and lays the foundation for rapid development of new features - both from the core team and external 3rd party extensions - enabling the community to extend llms.py in new unanticipated ways.
For deployments requiring minimal footprint, the Custom Build docs shows how to create a tailored distribution with only the specific extensions you need - perfect for CLI-only or lightweight API server deployments.
Extensions System
To keep the core lightweight while enabling limitless enhancements, we've implemented a flexible Extensions system inspired by ComfyUI Custom Nodes. This allows adding new features, pages and toolbar icons, register new provider implementations, extend, replace, and customize the UI with your own custom features, just by adding new extension folders.
Managing Extensions
List available extensions:
llms --addOutput:
Available extensions:
fast_mcp Add MCP Support using FastMCP
gemini Google Gemini RAG file search with document management, auto-upload & sync
xmas Example of utilizing the Extensions APIs to give llms.py some Christmas spirit
duckduckgo Add web search tool capabilities using Duck Duck Go
Usage:
llms --add <extension>
llms --add <github-user>/<repo>Install an extension:
llms --add fast_mcpInstall a 3rd-party extension:
llms --add my_user/my_extensionINFO
~/.llms/extensions/my_extension and installs any requirements.txt dependencies.List installed extensions:
llms --removeRemove an extension:
llms --remove fast_mcpManual Installation
Extensions can be installed from GitHub or by creating a local folder:
- Local: Simply create a folder in
~/.llms/extensions/my_extension - GitHub: Clone extensions into
~/.llms/extensions, e.g:
git clone https://github.com/user/repo ~/.llms/extensions/my_extensionSee Extensions docs for more details.
How it Works (Server)
Extensions are Python modules that plug into the server lifecycle using special hooks defined in their __init__.py:
| Hook | Purpose |
|---|---|
__parser__(parser) | Add custom CLI arguments |
__install__(ctx) | Enhance the server instance (routes, providers, filters, etc.) |
__load__(ctx) | Load data or perform async tasks before server starts |
__run__(ctx) | Execute custom logic when running in CLI mode |
The ctx parameter provides access to the ExtensionContext.
See Server Extensions docs for more details.
How it Works (UI)
Extensions can also include frontend components:
- Placement: Add a
uifolder within your extension directory - Access: Files in this folder are automatically served at
/ext/<extension_name>/* - Integration: Create a
ui/index.mjsfile. This is the entry point and must export aninstallfunction:
const MyComponent = {
template: `...`
}
// ui/index.mjs
export default {
install(ctx) {
// Register or replace components, add routes, etc.
ctx.components({ MyComponent })
}
}See UI Extensions docs for more details.
Example: xmas extension
The xmas extension demonstrates these capabilities where it utilizes the Extensions APIs to give llms.py a splash of Christmas spirit. It uses __install__ to register an API endpoint and a UI extension for its UI features.
Replacing Core Components
All UI features of xmas is implemented in its ui/index.mjs
which overrides default Brand and Welcome components by registering components with the same name, e.g:
const Brand = {
template: `
<div class="flex-shrink-0 p-2 border-b border-gray-200 dark:border-gray-700">
<button type="button" @click="$router.push('/')" class="...">
🎄 {{ $state.title }} 🎄
</button>
</div>
`,
}
const Welcome = {
template: `<!-- Custom Welcome Screen -->`,
setup() { /* ... */ }
}
export default {
install(ctx) {
ctx.components({
// Replaces built-in UI Components
Brand,
Welcome,
// Registers other custom components used in this UI Extension
XmasPage,
XmasTopPanel,
})
}
}To change both the home page and brand on the top-left to give every page title a festive touch:
It also demonstrates adding a new icon on the left sidebar to open its custom Xmas page component and a top-panel component to display its "Ask Santa" portal:
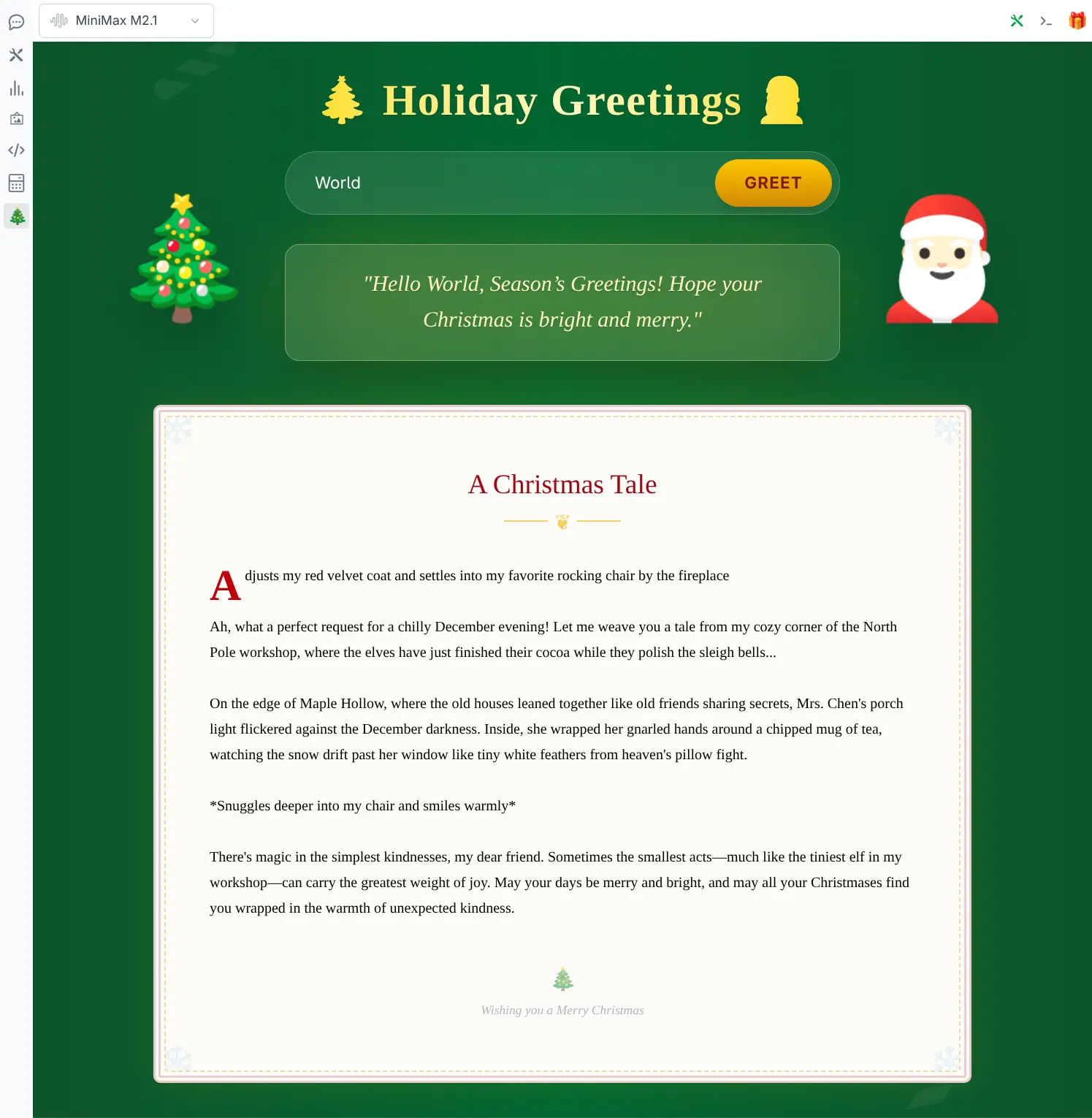
xmas page
Click to view full size
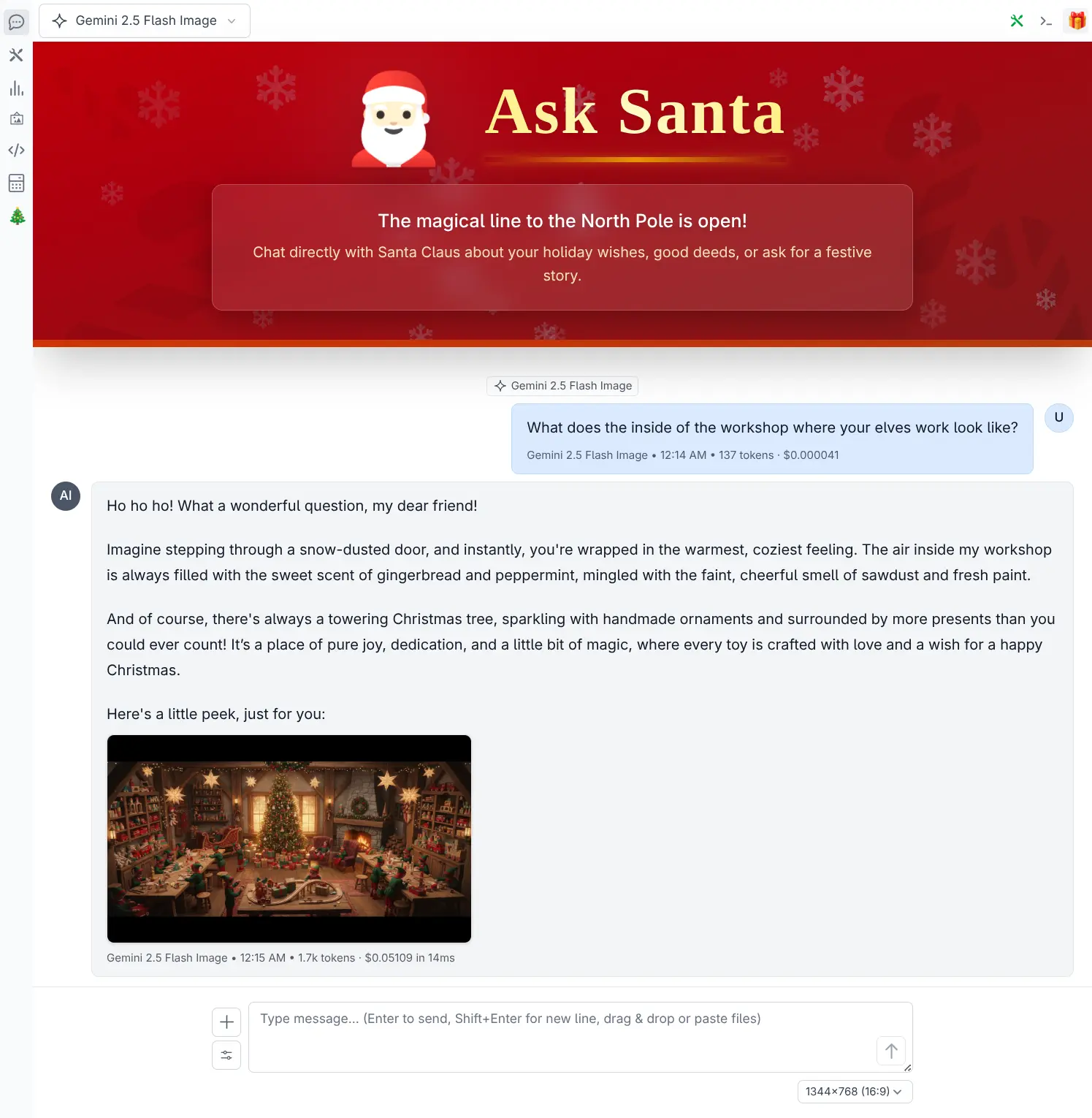
Ask Santa panel
Click to view full size
The Xmas page calls a custom API endpoint registered in its __install__ hook to return a custom festive greeting, whilst the top-panel modifies chat requests while its Top Panel is open to add a Santa system prompt which is enough to implement its "Ask Santa" feature.
Smart generation models like Nano Banana's gemini-2.5-flash-image perform exceptionally well here as they're able to answer your kids questions with rich, detailed responses and image outputs.
Gemini RAG Extension
The gemini extension provides a complete solution for managing Google Gemini's File Search Stores, enabling RAG (Retrieval Augmented Generation) workflows with automatic document uploads, category organization, and bidirectional sync between your local database and Gemini's cloud storage.
Build up your own knowledge base in File Stores, optionally organized into categories, that you can query to ground your AI chats with your own data - whether that's searching across a single document, a category of related documents, or your entire filestore.
Install
Install the gemini extension via the CLI:
llms --add geminiAfter which you'll be able to click the Gemini Icon to open the Gemini extension page from the sidebar to manage your filestores.
Key Features
- Filestore Management: Create and manage isolated stores of documents for different projects or knowledge bases
- Drag & Drop Uploads: Easily upload documents (PDF, Text, Markdown, etc.) by dragging them into the UI
- Smart Categorization: Organize documents into categories (folders) for granular retrieval
- Contextual RAG Chat:
- Ask Filestore: Chat with the entire knowledge base of a filestore
- Ask Category: Focus your chat on a specific category within a filestore
- Ask Document: Chat with a single specific document
- Bi-Directional Sync: Reconcile your local database with the remote Gemini File API
Uploading Documents
Documents can be uploaded by dragging and dropping files onto the upload zone or clicking to open the file picker. You can organize uploads into category folders by typing a category name before uploading.
Uploads are processed asynchronously by a Background Worker utilizing a DB Queue, so you can continue working while documents are indexed. The worker automatically starts when new documents are uploaded and efficiently handles batch processing without blocking the UI.
RAG Chat in Action
Once documents are uploaded, you can start contextual RAG chat sessions with your data. Each session is pre-configured with a Gemini Model and the file_search tool to query your selected filestore, category, or document - as shown in the meta example below querying this very v3 document for its best features:
The grounded sources used to answer your query are displayed at the bottom of each chat response, allowing you to verify and explore the source documents.
See the Gemini Extension docs for complete usage instructions.
Tool Support
This release also includes first-class support for Python function calling (Tools), allowing LLMs to interact with your local environment and custom functionality.
Tools can be defined using standard Python functions where its tool definition can be implicitly defined from its function's signature, type hints, and docstrings:
def get_current_time(tz_name: Optional[str] = None) -> str:
"""
Get current time in ISO-8601 format.
Args:
tz_name: Optional timezone name (e.g. 'America/New_York'). Defaults to UTC.
"""
if tz_name:
try:
tz = ZoneInfo(tz_name)
except Exception:
return f"Error: Invalid timezone '{tz_name}'"
else:
tz = timezone.utc
return datetime.now(tz).isoformat()Register tools for function calling
Implicit Tool Definition
Tools can be registered within an extension's install hook using ctx.register_tool:
def install(ctx):
# Automatic definition from function signature
ctx.register_tool(get_current_time)If no group is specified, tools are registered under the default custom group, alternatively you can group them under your preferred name:
ctx.register_tool(get_current_time, group="my_tools")Explicit Tool Definition
When more fine-grain configuration is needed you can use an explicit tool definition, e.g:
ctx.register_tool(
get_current_time,
{
"type": "function",
"function": {
"name": "get_current_time",
"description": "Get current time in ISO-8601 format.",
"parameters": {
"type": "object",
"properties": {
"tz_name": {
"type": "string",
"description": "timezone name (e.g. 'America/New_York')",
"default": "UTC"
}
},
"required": []
}
}
})UI Management
- One-Click Enable/Disable: Use the Tool Selector in the top-right to control which tools to use per request
- Granular Control: Select "All", "None", or specific tools for each chat session
Dedicated Tools Page: View all registered tools and their definitions at /tools or via the sidebar
MCP Support
The fast_mcp extension brings Model Context Protocol (MCP) support to llms.py, allowing you to extend LLM capabilities with a wide range of external tools and services using the FastMCP Python Framework.
Install
llms --add fast_mcpKey Features
- Standardized Tool Access: Connect to any MCP-compliant server (Node.js, Python, etc.) seamlessly
- Dynamic Discovery: Automatically discovers and registers all tools exposed by configured servers
- Parallel Discovery: All configured MCP servers are discovered concurrently for fast startup times
- UI Management: Add, edit, and manage MCP servers directly from the Tools page
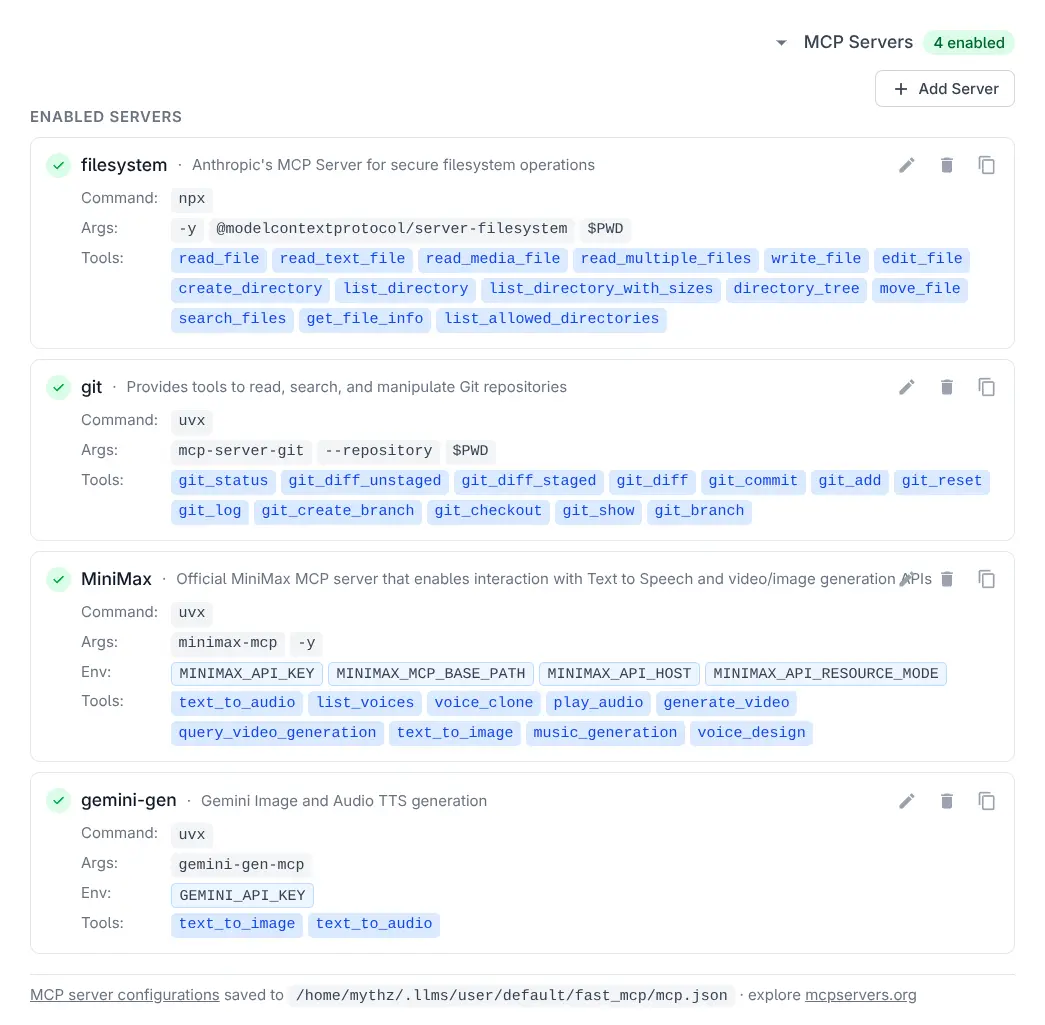
MCP Servers
Click to view full size
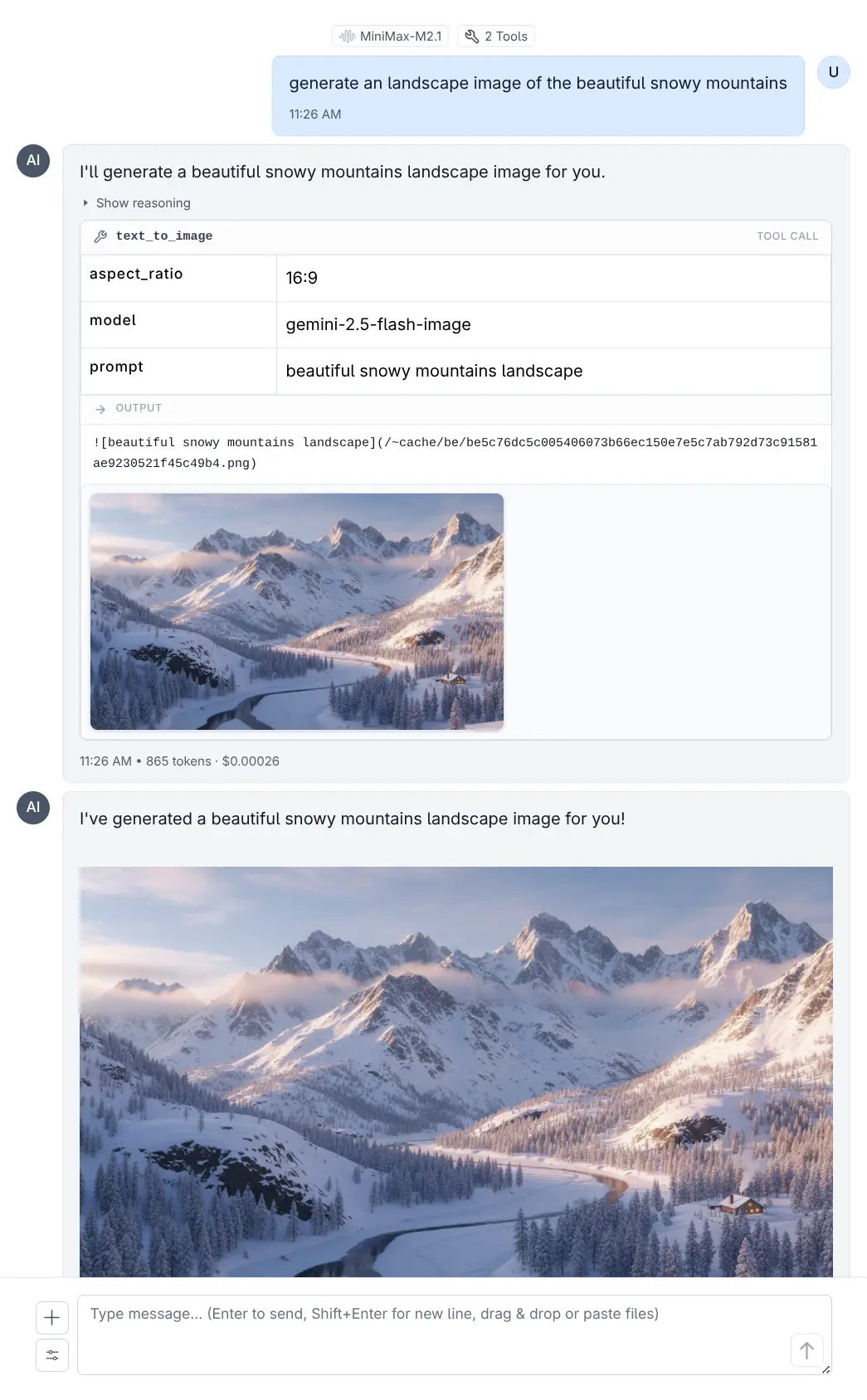
Gemini Image via MCP
Click to view full size
Configuration
MCP servers are configured via a mcp.json file. By default, Anthropic's Git MCP Server is pre-configured:
{
"mcpServers": {
"git": {
"command": "uvx",
"args": ["mcp-server-git", "--repository", "$PWD"]
},
"gemini-gen": {
"description": "Gemini Image and Audio TTS generation",
"command": "uvx",
"args": ["gemini-gen-mcp"],
"env": {
"GEMINI_API_KEY": "$GEMINI_API_KEY"
}
}
}
}Managing Servers
Add, edit, or remove MCP servers directly from the UI:
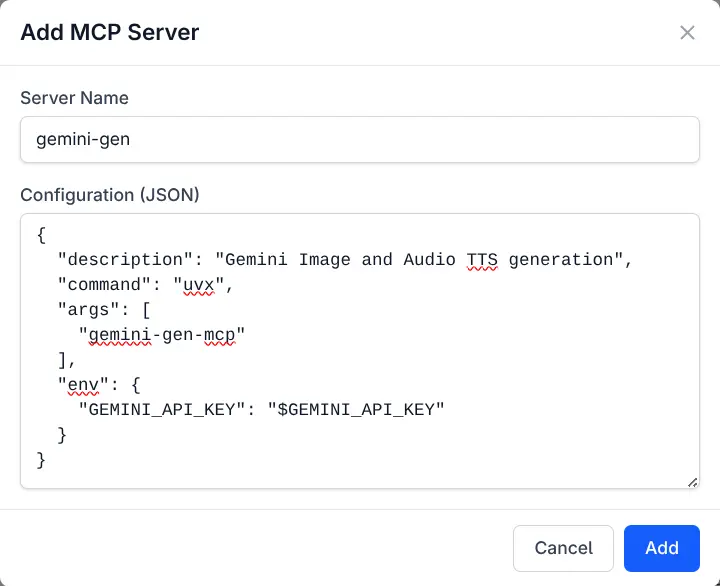
Add MCP Server
Click to view full size
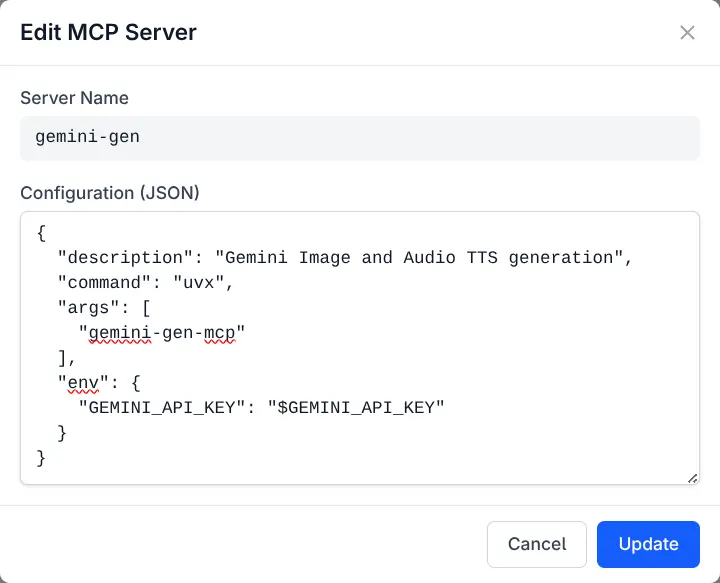
Edit MCP Server
Click to view full size
Executing Tools
MCP tools can be executed directly from the Tools page or invoked by LLMs during chat sessions:
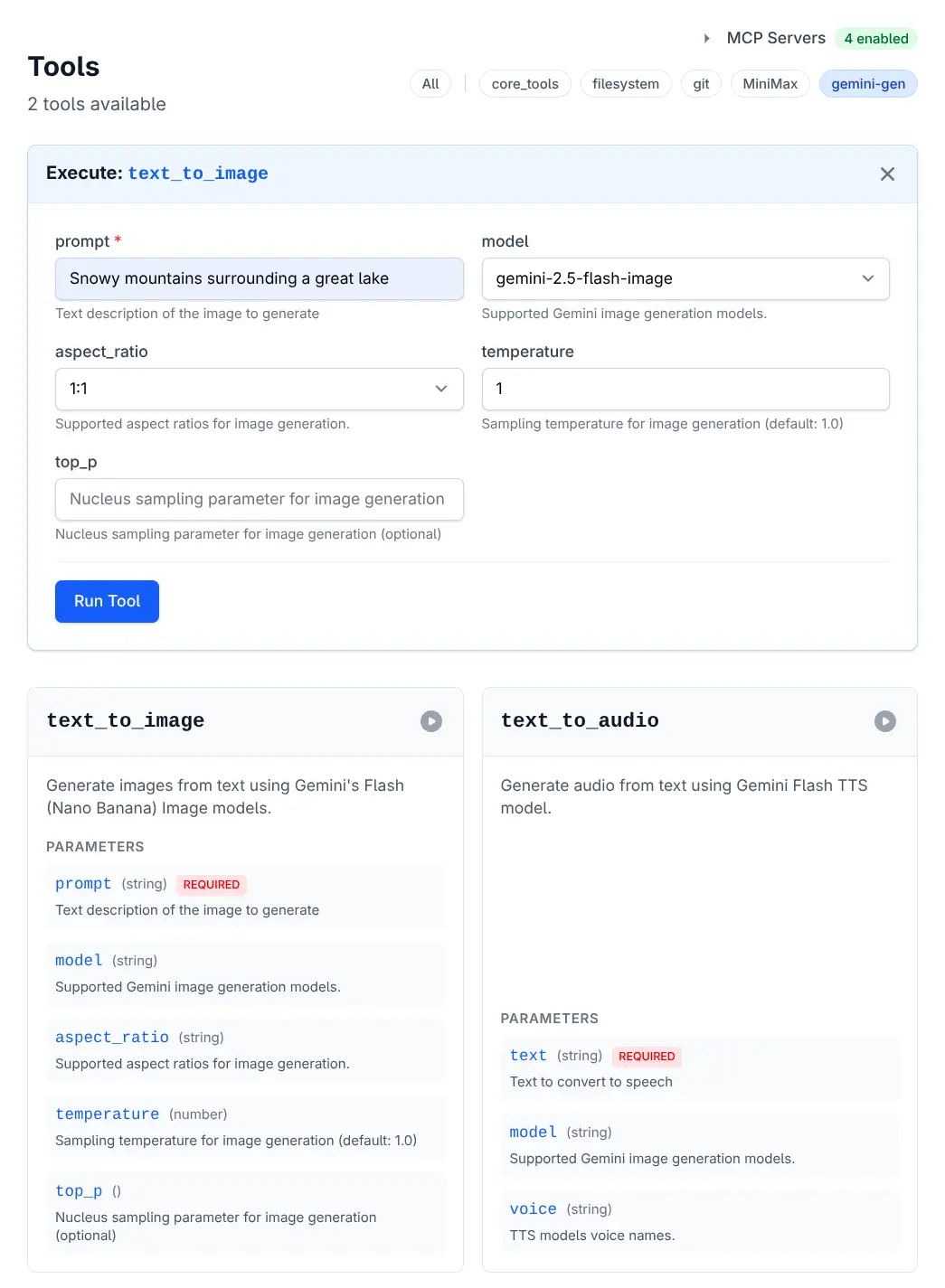
Execute Tool
Click to view full size
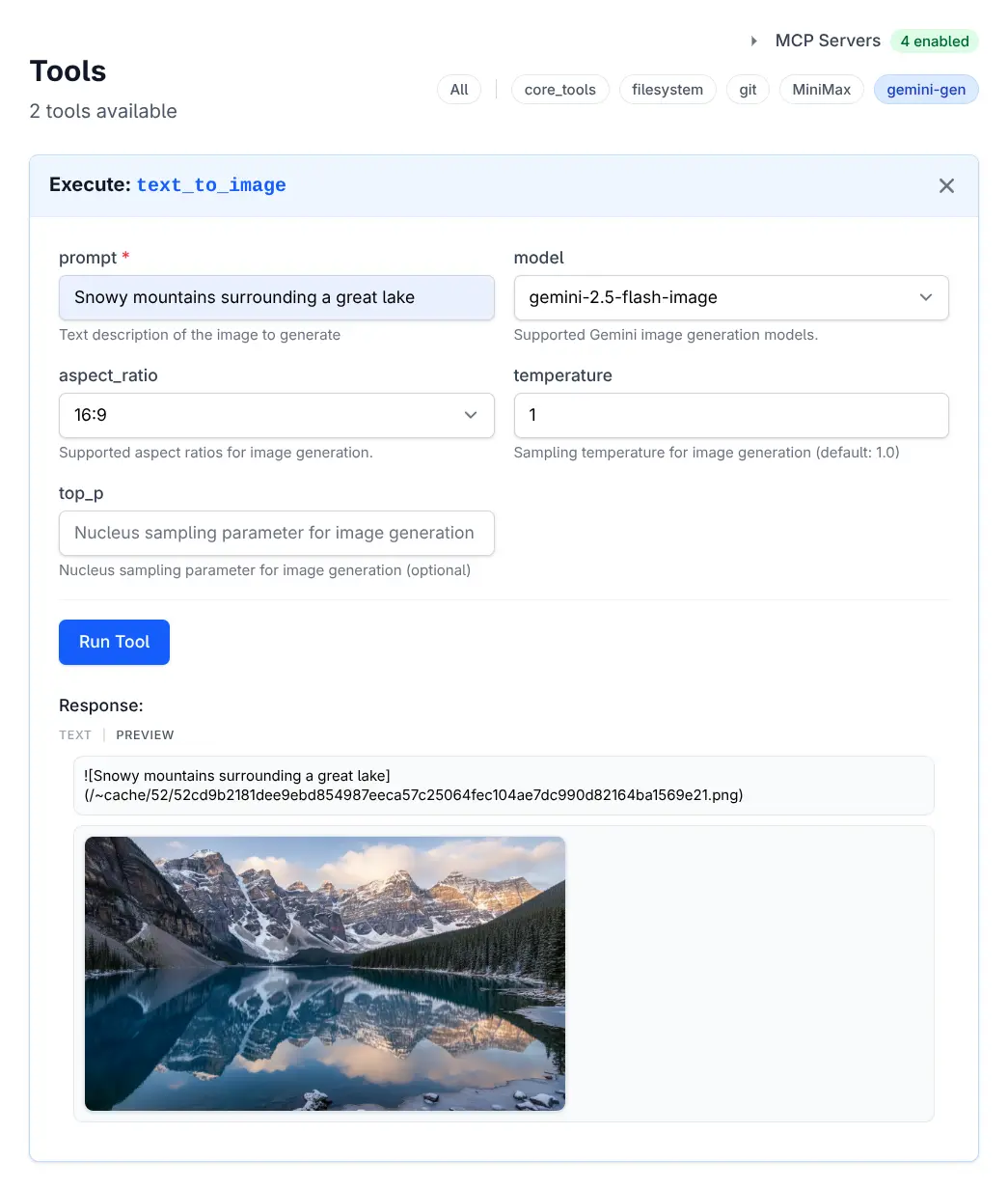
Tool Results
Click to view full size
HTML Results
Tool outputs containing HTML content are rendered within a sandboxed iframe, letting you interact with rich content and even play games:
See the MCP Support docs for complete configuration and usage details.
Omarchy MCP
For Omarchy users, the Omarchy MCP enables AI assistants to manage themes - including listing, switching, previewing, installing, and removing themes from your Omarchy desktop environment.
Core Tools
The built-in core_tools extension provides essential functionality for LLMs to interact with their environment, perform calculations, and manage persistent data.
Utilities
get_current_time- Get the current time in ISO-8601 format.
Math & Logic
calc- Evaluate a mathematical expression. Supports arithmetic, comparison, boolean operators, and common math functions.
Code Execution Tools
LLMS includes a suite of tools for executing code in various languages within a sandboxed environment. These tools are designed to allow the agent to run scripts, perform calculations, and verify logic safely.
Supported Languages
run_python(code)- Executes Python code.run_javascript(code)- Executes JavaScript code (usesbunornode).
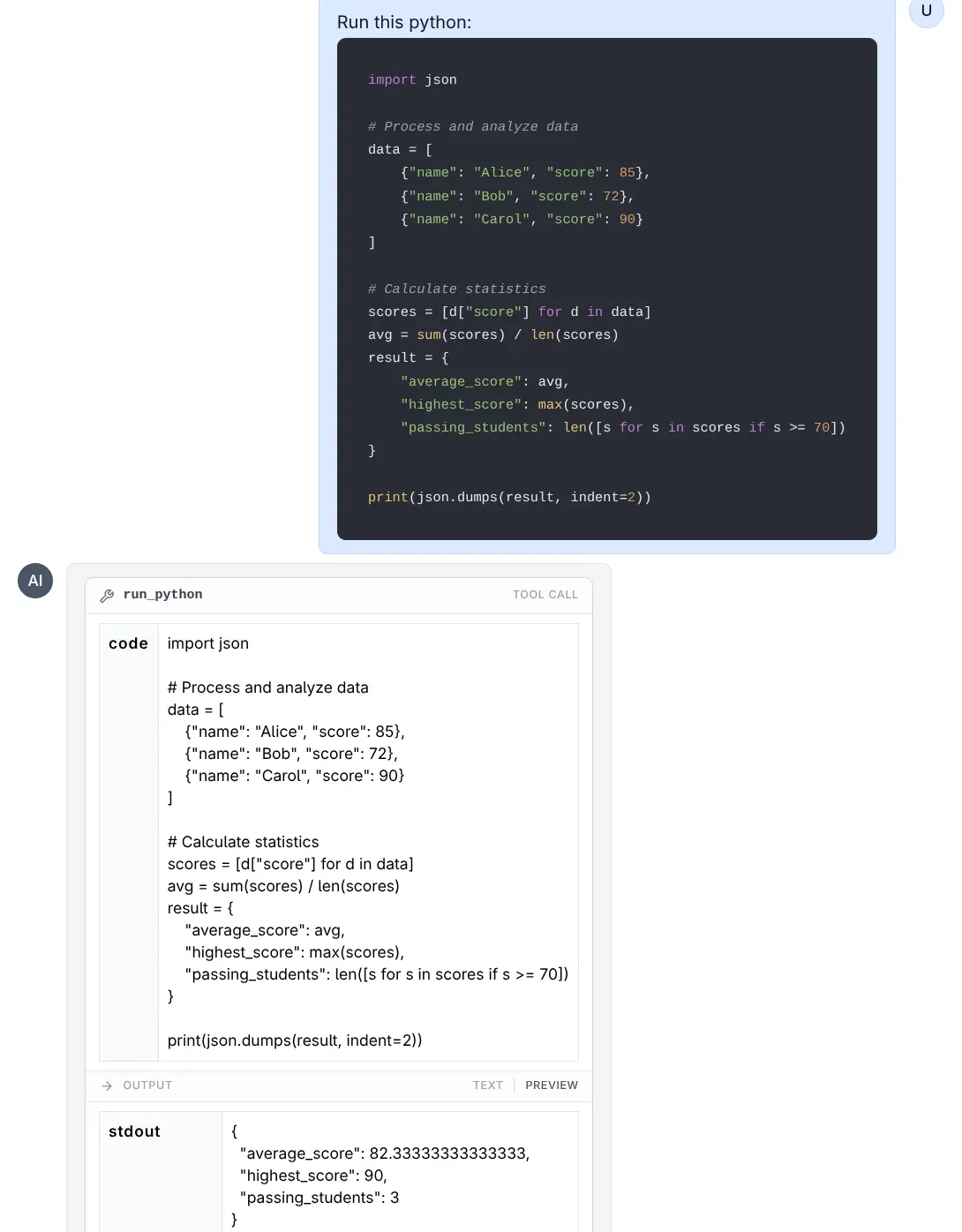
Run Python
Click to view full size
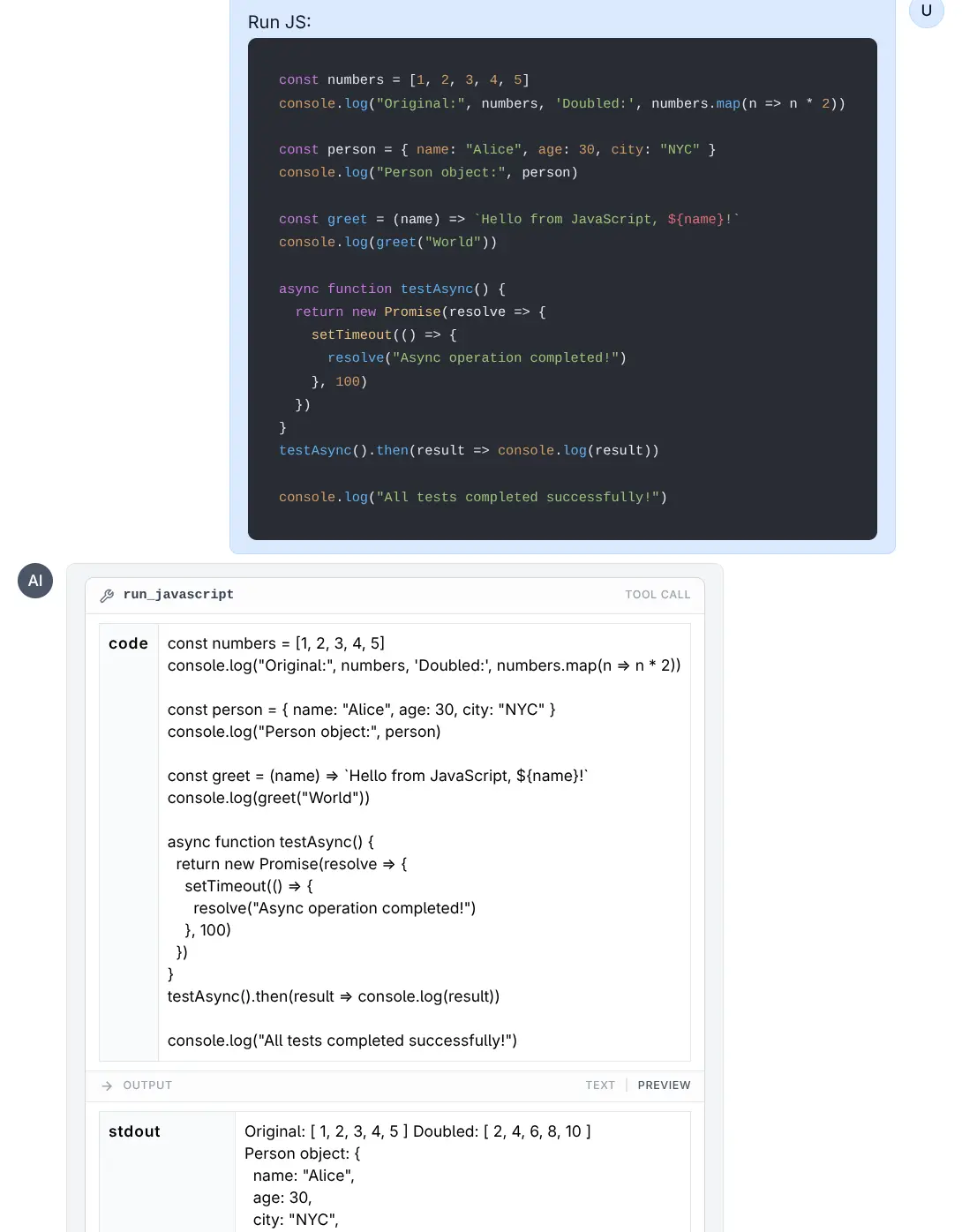
Run JavaScript
Click to view full size
run_typescript(code)- Executes TypeScript code (usesbunornode).run_csharp(code)- Executes C# code (usesdotnet runwith .NET 10+ single-file support).
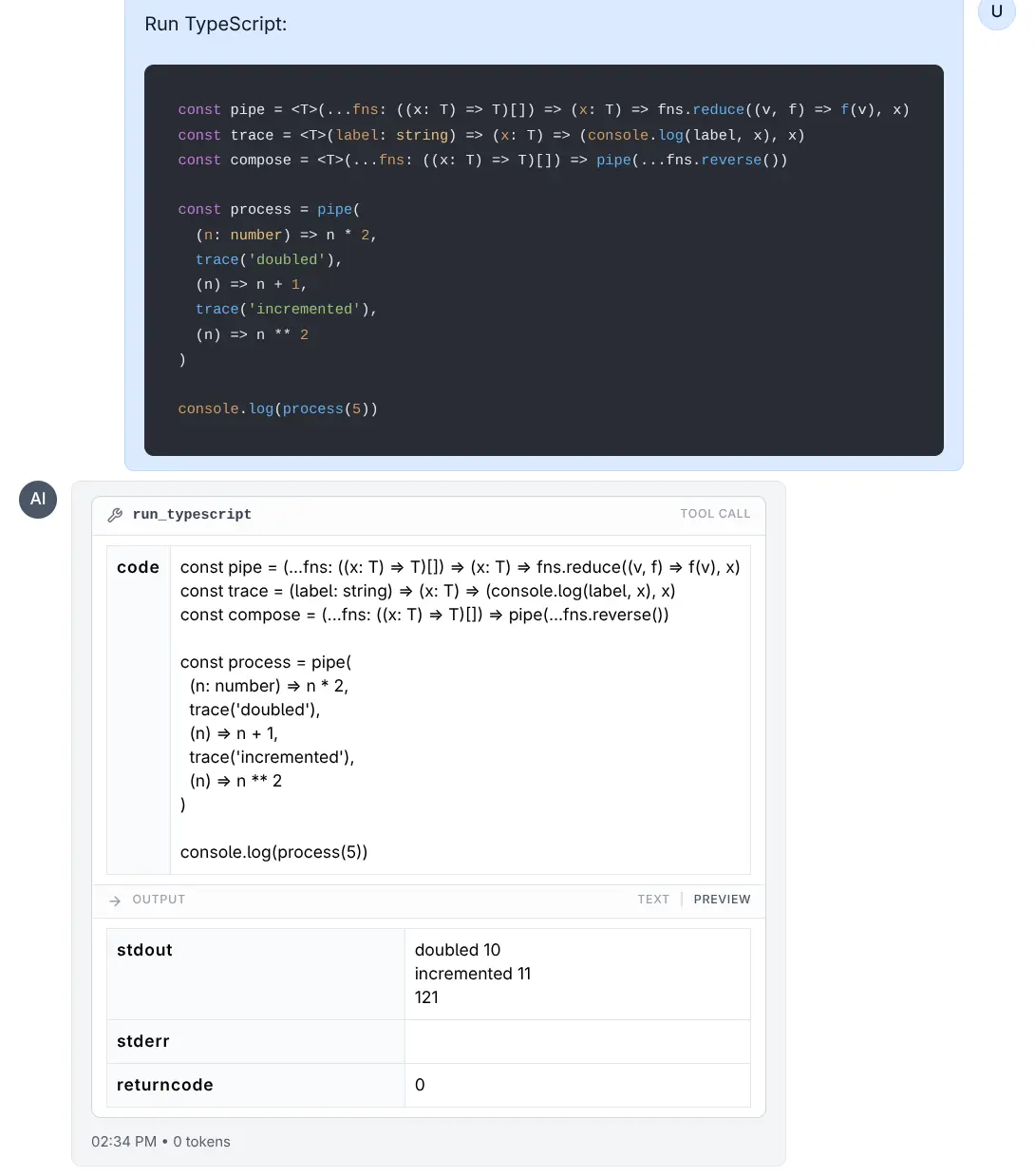
Run TypeScript
Click to view full size
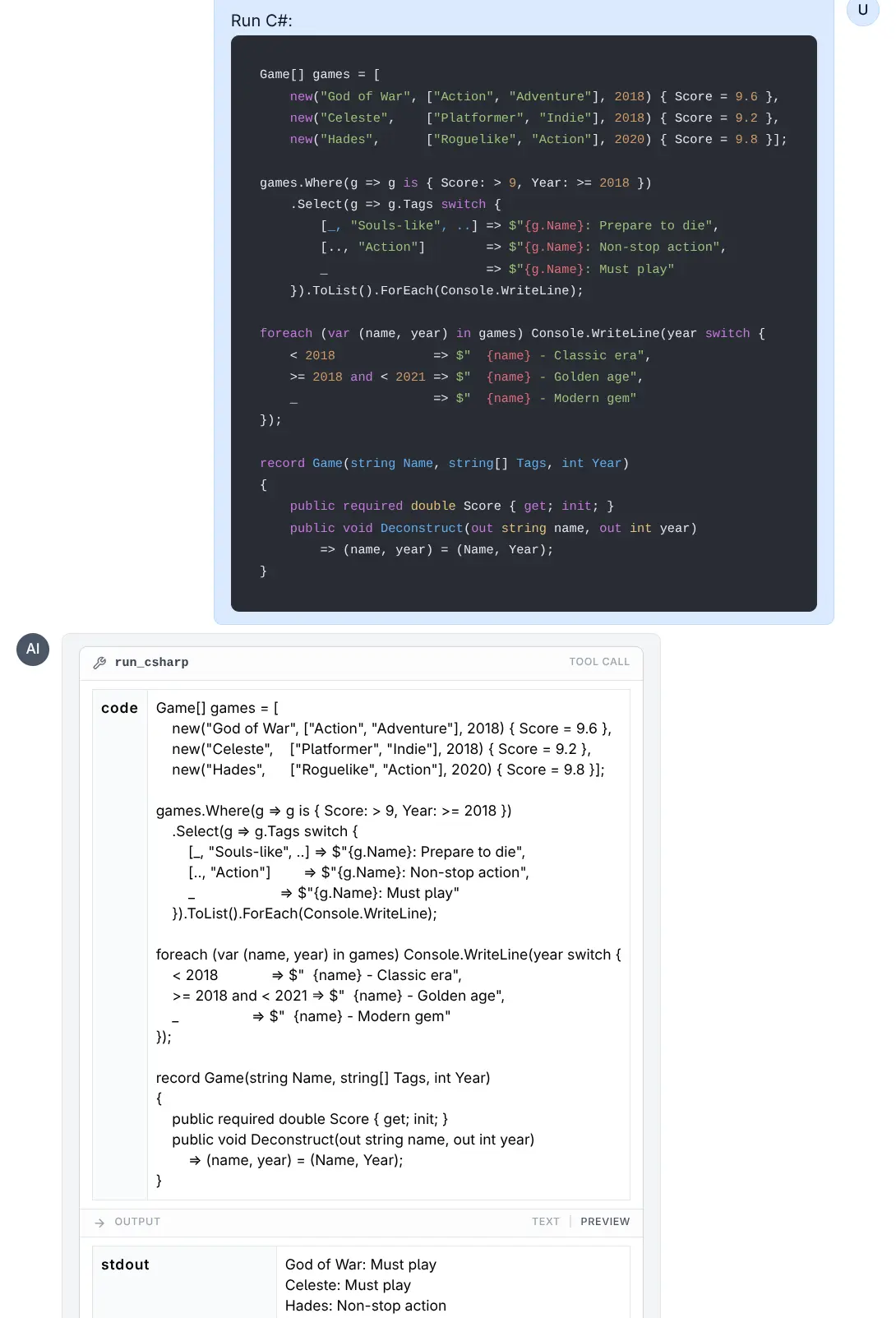
Run C#
Click to view full size
File System Tools
The built-in computer extension filesystem.py tools provide a native Python implementation of Anthropic's node.js Filesystem MCP Server tools which allow LLMs to interact with the local file system in a safe and controlled manner enabling reading, writing, and searching of allowed files and directories only.
read_text_file- Read complete contents of a file as textread_media_file- Read an image or audio fileread_multiple_files- Read multiple files simultaneouslywrite_file- Create new file or overwrite existing (exercise caution with this)edit_file- Make selective edits using advanced pattern matching and formattingcreate_directory- Create new directory or ensure it existslist_directory- List directory contents with [FILE] or [DIR] prefixeslist_directory_with_sizes- List directory contents with [FILE] or [DIR] prefixes, including file sizesmove_file- Move or rename files and directoriessearch_files- Recursively search for files/directories that match or do not match patternsdirectory_tree- Get recursive JSON tree structure of directory contentsget_file_info- Get detailed file/directory metadatalist_allowed_directories- List all directories the server is allowed to access
Computer Use
The built-in computer extension transforms AI agents into autonomous computer operators. Based on Anthropic's computer use tools, it enables agents to see your screen, control the mouse and keyboard, execute shell commands, and edit files - just like a human sitting at the computer.
This unlocks powerful capabilities that traditional API-based tools cannot achieve:
- Visual Verification: Confirm that code actually renders correctly in a browser
- Desktop Automation: Control any GUI application - web browsers, IDEs, terminals
- End-to-End Workflows: Chain together multiple applications in a single task
- Legacy Applications: Automate software that lacks APIs
For example, an agent can write a web application, open a browser, and capture a screenshot to prove it works:
See the Computer Use docs for complete usage details.
Calculator UI
As some core tools are particularly useful on their own, dedicated UIs has been added for the calc tool with support for evaluating mathematical python expressions, including arithmetic, comparison, boolean operators, math.* functions & constants and python list comprehensions
- 🖥️ UX Friendly Interface - Clean, modern, responsive UI with dark mode support
- 💾 Persistent History - Calculations automatically saved to localStorage and preserved between sessions
- ⚡ 1-Click Interaction - Click history items to instantly load expressions and copy to clipboard
- ⌨️ Keyboard-Free Access - Complete UI buttons for numbers, operators, constants, and math functions
- 🐍 Python Math Support - Full access to Python's math library including trig, stats, and more
- 🛡️ Safe Evaluation - AST-based evaluator prevents arbitrary code execution for secure calculations
Run Code UI
Whilst the run_python tools provides a scratch pad for running stand-alone Python, JavaScript, TypeScript, and C# code in a sandbox.
The UI uses CodeMirror as the code editor, providing a better user experience with syntax highlighting, code completion, and other IDE-like features for writing code.
Run Python, JavaScript, TypeScript & C# programs
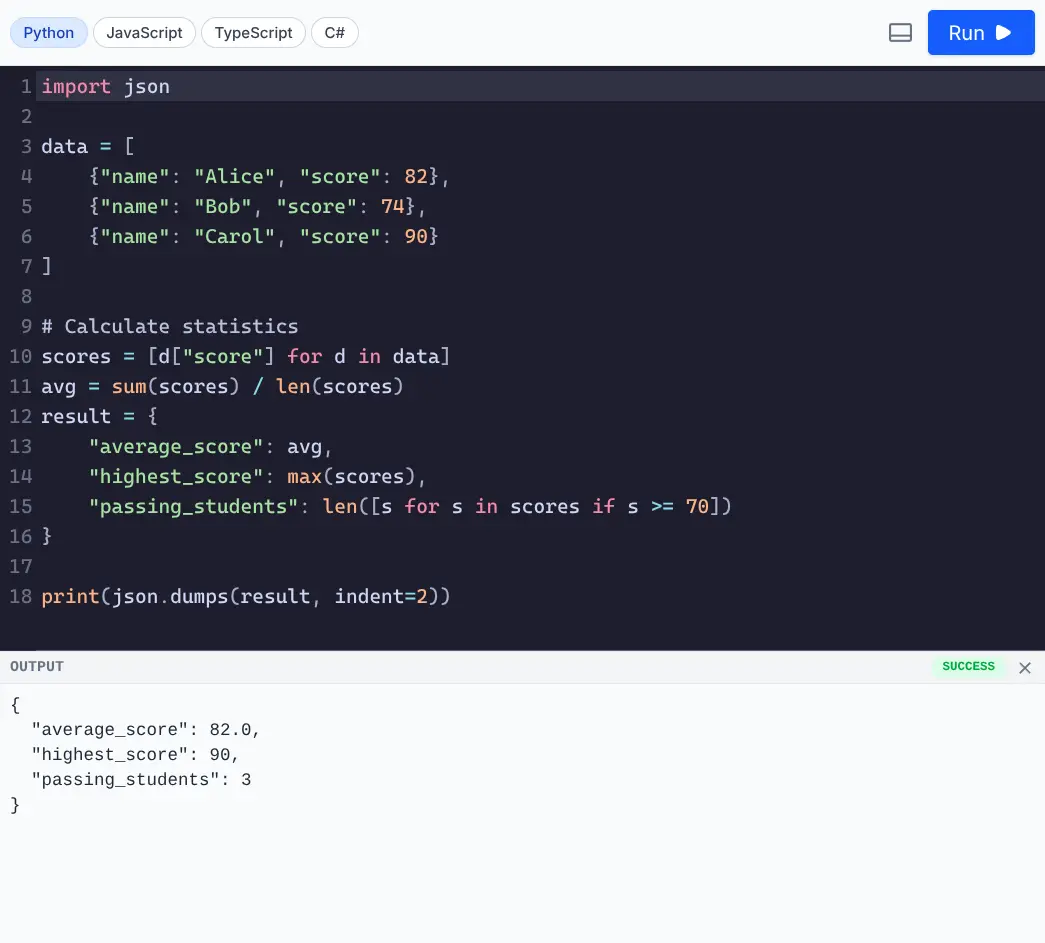
Run Python
Click to view full size
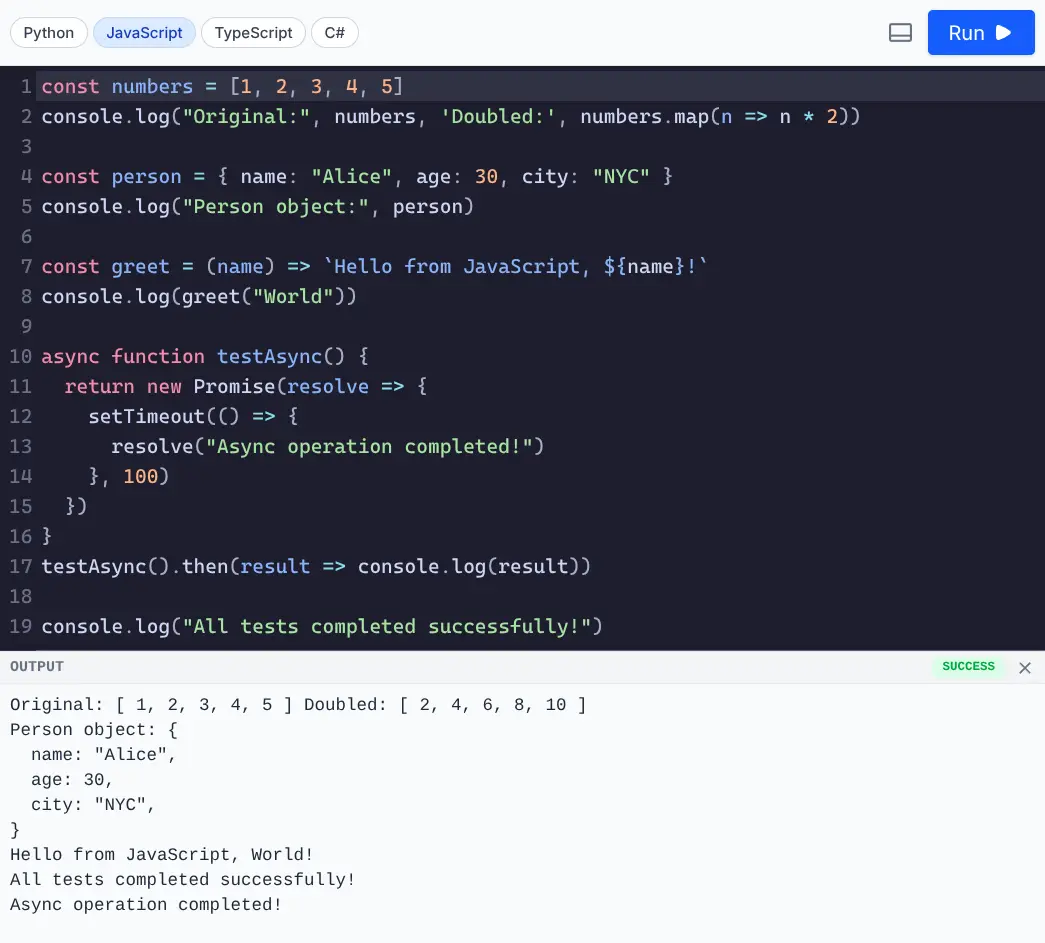
Run JavaScript
Click to view full size
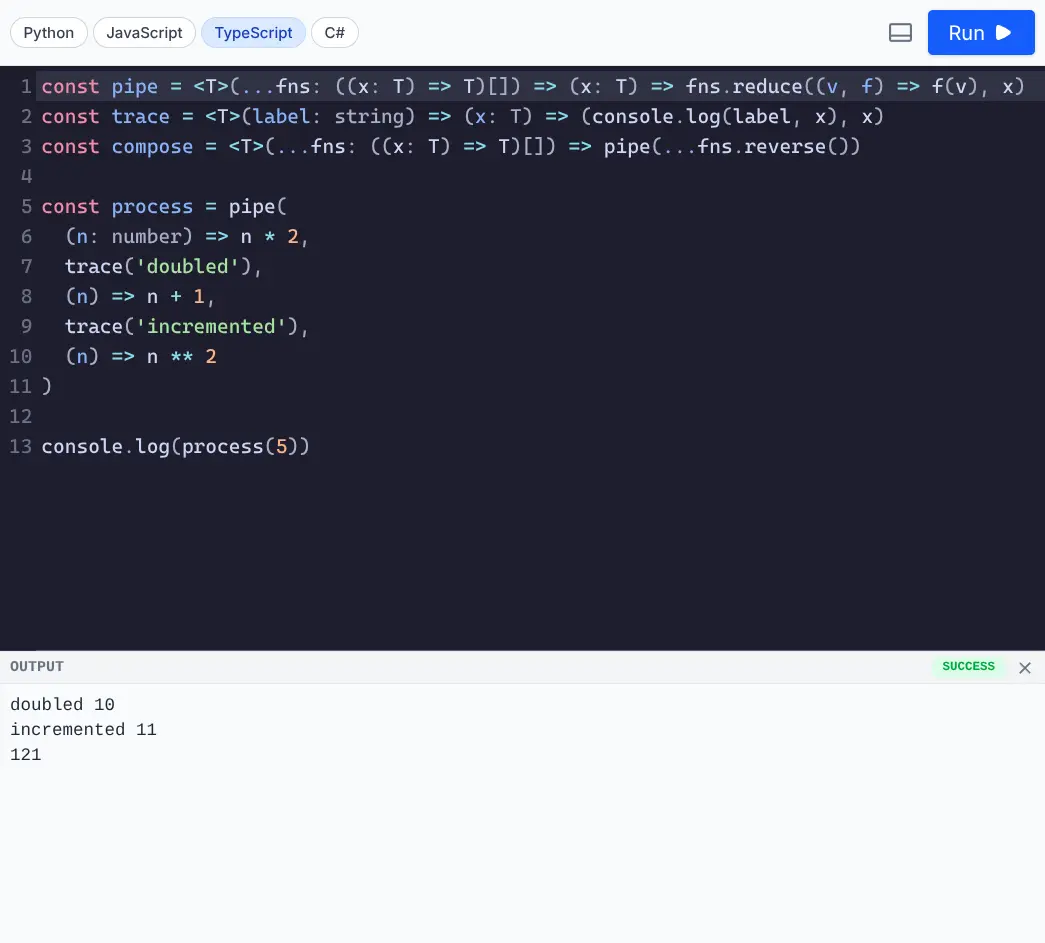
Run TypeScript
Click to view full size
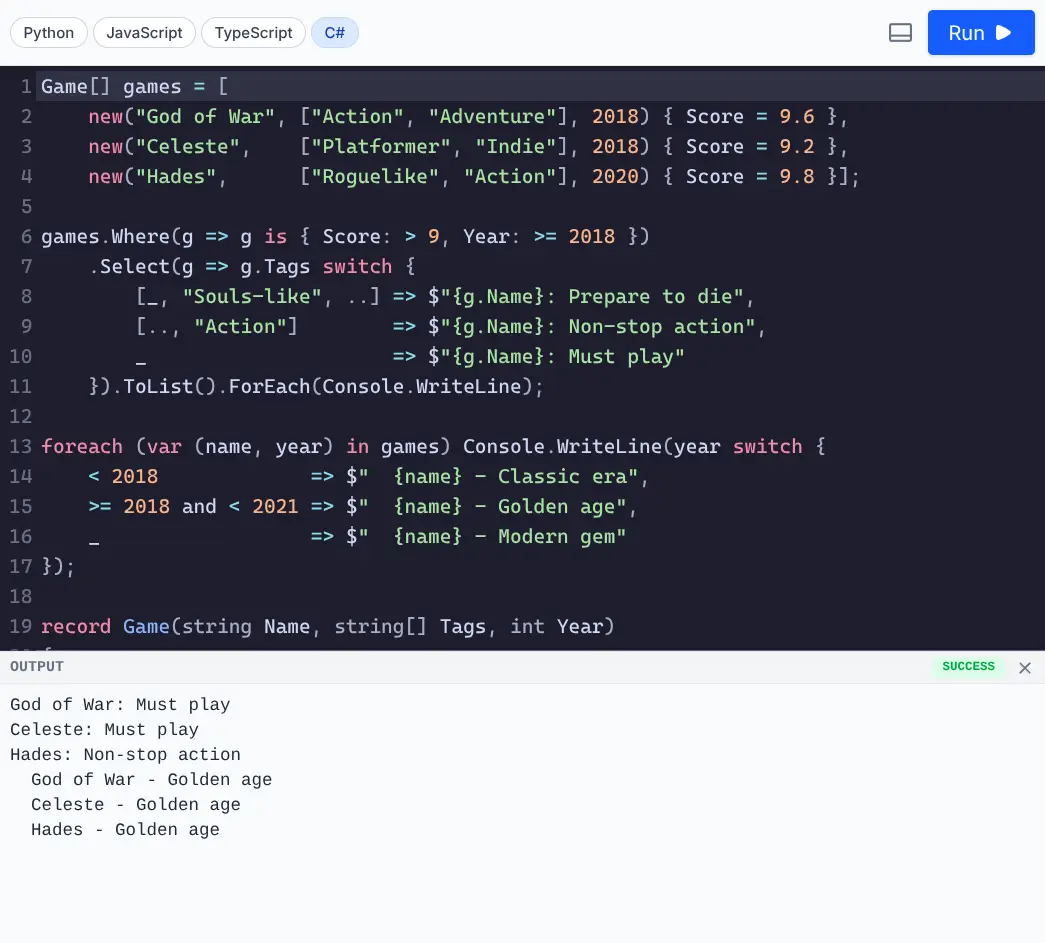
Run C#
Click to view full size
The UI uses CodeMirror as the code editor, providing a better user experience with syntax highlighting, code completion, and other IDE-like features for writing code.
INFO
See the Run Code UI docs for more details.
KaTeX Math Typesetting
The katex extension enables beautiful rendering of LaTeX math expressions in AI responses using KaTeX. It integrates automatically with the markdown parser to render math equations in both inline and block formats.
Features
- Fast Rendering: Uses KaTeX for high-performance rendering of math expressions.
- Inline Math: Renders math within text using
$or$$delimiters. - Block Math: Renders complex equations in their own block using
$or$$delimiters across multiple lines. - Auto-Integration: Automatically extends the
markedparser used in the application.

Popular math expressions
Click to view full size

Basic math expressions
Click to view full size
Image Generation Support
Unlike text generation, there's no standard API for image generation across providers - each requires its own custom implementation. Despite the additional effort required, there's now seamless image generation support through both the UI and CLI with built-in integrations for:
| Provider | Status |
|---|---|
| ✅ Supported | |
| OpenAI | ✅ Supported |
| OpenRouter | ✅ Supported |
| Chutes | ✅ Supported |
| Z.ai | ✅ Supported |
| Nvidia | ✅ Supported |
To begin select an image generation model from the Model Selector that supports image generation:
When an image generation model is selected, the chat prompt will the option to specify which aspect ratio to use for the generated images:
Command-Line Usage
Generate images using the --out image modifier:
llms --out image "cat in a hat"Which uses the out:image chat template in llms.json for its image generation request. Before returning, any assets are saved to cache and their local path and HTTP URL returned, e.g:
Output:
Here is a cat in a hat for you!
Saved files:
/home/mythz/.llms/cache/c9/c9b2fd2a1d95708251...5d3f467a.png
http://localhost:8000/~cache/c9/c9b2fd2a1d95708251...5d3f467a.pngSpecify a Model
Use any model that supports image generation by specifying its ID or name:
llms -m "gemini-2.5-flash-image" --out image "cat in a hat"
llms -m "Gemini 2.5 Flash Image" --out image "cat in a hat"INFO
~/.llms/cache using their SHA-256 hash as the filename.Audio Generation Support
Audio generation is an emerging capability with limited provider support where Text-to-Speech generation through both the UI and CLI, currently only supports Google's latest TTS models:
| Model | Description |
|---|---|
| Gemini 2.5 Flash Preview TTS | Fast, lightweight TTS |
| Gemini 2.5 Pro Preview TTS | High-quality TTS |
Typically you'd select the audio generation model from the Model Selector to find models that supports audio generation:
But despite models.dev listing them as capable of audio generation, only Gemini's TTS models are currently supported for audio generation through Gemini's API as Alibaba doesn't yet support the audio modality.
UI & Command-Line Usage
Available in both the UI and on the command-line using --out audio:
llms --out audio "Merry Christmas"
llms -m gemini-2.5-pro-preview-tts --out audio "Merry Christmas"Output
Audio files are saved locally and accessible via HTTP URL:
Saved files:
/Users/llmspy/.llms/cache/c2/c27b5fd43ebbdbca...acf118.wav
http://localhost:8000/~cache/c2/c27b5fd43ebbdbca...acf118.wavPlayback
From the command line:
play /Users/llmspy/.llms/cache/c2/c27b5fd43ebbdbca...acf118.wavFrom the browser:
Run server with llms --serve 8000 to play URL in your browser.
Media Gallery
The gallery extension intercepts all generated image, audio & file assets and uploaded files in ~/.llms/cache file storage whose metadata is maintained in a SQLite database at ~/.llms/user/default/gallery/gallery.sqlite
Dedicated UIs are available for quickly browsing and navigating or generated images / audio files including a lightbox previewer for full-size viewing:
Portrait Images
Square Images
Landscape Images
Audio Generations
System Prompts Library
System prompts support was refactored into a replaceable system_prompts extension which configures AI requests with a library of over 200+ awesome curated system prompts that can be selected from the UI.
Custom System Prompts
You can maintain your own library of system prompts for all anonymous users at:
~/.llms/user/default/system-prompts.json
Or for signed in users at:
~/.llms/user/<github-user>/system-prompts.json
With the JSON file simply containing an array of names and their system prompts, e.g:
[
{
"name": "Helpful Assistant",
"prompt": "You are a helpful assistant."
}
]Browse the complete collection of available system prompts below:
Server SQLite and Cached File Storage persistence
Another major change is the migration from client-side IndexedDB storage to a robust server-side SQLite databases. This architectural shift ensures better data consistency, improved performance that enables parallel executions and multi-device access to your chat history.
To keep the database efficient and portable, binary assets (images, audio, etc.) are not stored directly in the SQLite database, Instead all generated assets are stored in the local file system cache at ~/.llms/cache and only relative URLs referencing these assets are stored in the database.
Concurrency Model
To ensure data integrity and high performance without complex locking mechanisms, the system utilizes a single background thread to write operations to the database. This design improves concurrency handling and eliminates database locking issues during high-load scenarios.
Multi-Tenancy & Security
When authentication is enabled, data isolation is automatically enforced. All core tables, including threads and requests, are scoped to the authenticated user, ensuring that users can only access their own data.
Image Cache & Optimization
A new caching system has been implemented for generated assets and uploaded images and files that's now persisted in ~/.llms/cache, preserving them across messages and sessions.
- Efficient Storage: Only cache references are stored with chat messages
- Persistent Access: Images remain accessible in previews and downloads after page reloads
- Automatic Management: System handles file storage and serving transparently
Now that all persistence is server-side, to transfer or backup your configurations, extensions and Chat History you need only copy your ~/.llms folder.
CLI - more Powerful than Ever
All server extension features including tools, custom providers, database persistence, and image/audio generation are fully accessible via the command line, making llms.py a powerful terminal-based AI assistant.
Core CLI Usage
# One-shot query
llms "What is the capital of France?"
# Specify model by ID or name
llms -m claude-opus-45 "Explain quantum computing"
llms -m "Claude Opus 4.5" "Write a Python function"Tools & Function Calling
All registered tools are automatically available in CLI mode. Enable specific tools with the --tools flag:
# Use all available tools by default (`--tools all`)
llms "Read the file data.txt and calculate the sum"
# Use specific tools
llms --tools calc,get_current_time "What time is it in Tokyo and what's 15% of 230?"
# Don't use any tools
llms --tools none "Tell me a joke"Extensions Management
# List available extensions from github.com/llmspy
llms --add
# Install an extension
llms --add fast_mcp
# Install a 3rd-party extension from GitHub
llms --add github-user/repo-name
# List installed extensions
llms --remove
# Uninstall an extension
llms --remove fast_mcpProvider Management
# List all enabled providers and models
llms ls
# List available models from a specific provider
llms ls google
# Enable a provider
llms --enable google
# Disable a provider
llms --disable google
# Update provider definitions from models.dev (automatically updated daily)
llms --update-providersImage Analysis, Audio Transcribing & Documents Processing
# Image Analysis
llms --image https://example.com/chart.jpg "Analyze this chart"
# Audio Processing
llms -m gpt-4o-audio-preview --audio interview.mp3 "Transcribe this interview"
# Document Processing
llms -m gpt-5 --file report.pdf "Extract action items"Media Generation
Generate images and audio directly from the command line:
# Generate images
llms --out image "A serene mountain landscape at sunset"
llms -m "gemini-2.5-flash-image" --out image "Logo for a tech startup"
# Generate audio
llms --out audio "Welcome to our podcast"
llms -m gemini-2.5-pro-preview-tts --out audio "Hello world"All generated media is automatically saved to ~/.llms/cache with metadata persisted in SQLite.
Database Persistence
All CLI interactions are automatically persisted to ~/.llms/user/app/app.sqlite, including:
- Chat threads and messages
- Tool calls and results
- Generated assets and file references
- User preferences and settings
Ensuring your conversation history is preserved and accessible from both CLI and Web UI.
Server Mode
Launch the web UI while keeping full CLI access:
# Start UI and Chat Completion API on port 8000
llms --serve 8000See CLI Docs for more details.
Upgrade Instructions
# Update llms to v3
pip install llms-py --upgrade
# Upgrade any external extensions
llms --update all
# Start the server
llms --serve 8000Happy holidays from llms.py! 🎄
Building a Community Extension Ecosystem
With llms .py rebuilt from the ground up as an extensible platform, we hope to foster a thriving community extension ecosystem where developers can share innovative solutions and extend llms.py in ways we haven't yet imagined.
As llms .py is still in active development, we welcome your feedback on any features that would better support 3rd party extensions and help cultivate this growing community.